File:PipeResistanceRe51b.png
Original file (1,517 × 560 pixels, file size: 28 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Summary
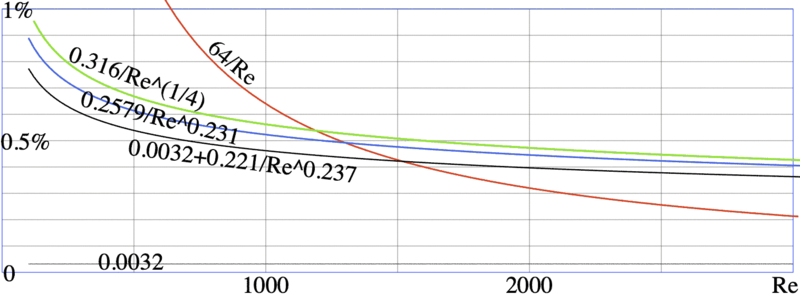
Various approximations for the hydrodynamic resistance of a pipe versus the Reynolds number.
The formulas are from Ruvika
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Формула_Дарси_—_Вейсбаха
Dp = lambda L V^2 /(2 D) rho
Lamimar: Lambda = 64/Re
Blasius: 0.316 Re^(-1/4)
Nikuradze: 0.0032 + 0.221 Re^(-0.237)
Kantakuzen: 0.2579 Re^(-0.231)
density = density_0 P/P_0
V= sqrt(P' R / Lambda)
Extraction command:
convert -colors 9 51.png 51b.png; ls -al ; open 51b.png
PHP generator
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"/></head>
<body>
<svg width="3080" height="1200">
<polygon points="10,110 3010,110 3010,1110 10,1110"
style="fill:none;stroke:#00f;stroke-width:2" />
<?php
$X0=10; $Y0=1110;
for($x=500; $x<3000; $x+=500){echo '<polyline points="';
printf("%1.0f,%1.0f %1.0f,%1.0f",$X0+$x, $Y0, $X0+$x,$Y0-1000);
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#000;stroke-width:1"/>';}
for($y=100; $y<1100;$y+=100){echo '<polyline points="';
printf("%1.0f,%1.0f %1.0f,%1.0f",$X0, $Y0-$y, $X0+3000,$Y0-$y);
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#000;stroke-width:1"/>';}
echo '<polyline points="';
for($x=500; $x<3060; $x+=40){ $y=64/$x;
printf("%1.0f,%3.2f ",$X0+$x, $Y0-10000*$y); }
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#F00;stroke-width:6"/>';
echo '<polyline points="';
for($x=120; $x<3060; $x+=20){ $y=.316/sqrt(sqrt($x));
printf("%1.0f,%3.2f ",$X0+$x, $Y0-10000*$y); }
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#0e0;stroke-width:7"/>';
echo '<polyline points="';
for($x=100; $x<3060; $x+=20){ $y=0.2579/pow($x,0.231);
printf("%1.0f,%3.2f ",$X0+$x, $Y0-10000*$y); }
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#06f;stroke-width:6"/>';
echo '<polyline points="';
for($x=100; $x<3060; $x+=20){ $y=0.0032 + 0.221/pow($x,0.237);
printf("%1.0f,%3.2f ",$X0+$x, $Y0-10000*$y); }
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#000;stroke-width:5"/>';
echo '<polyline points="';
for($x=100; $x<3101; $x+=2900){ $y=0.0032;
printf("%1.0f,%3.2f ",$X0+$x, $Y0-10000*$y); }
echo '" style="fill:none;stroke:#000;stroke-width:2"/>';
?>
<g font-size="90" font-family="times" fill=#000 stroke="none" text-anchor="middle">
<text x="70" y="144">1%</text>
<text x="100" y="644">0.5%</text>
<text x="40" y="1144">0</text>
<text x="1010" y="1188">1000</text>
<text x="2010" y="1188">2000</text>
<text x="2980" y="1188">Re</text>
<text x="880" y="-300" transform="rotate(40)">64/Re</text>
<text x="620" y="200" transform="rotate(20)">0.316/Re^(1/4)</text>
<text x="720" y="390" transform="rotate(14)">0.2579/Re^0.231</text>
<text x="1000" y="600" transform="rotate(7)">0.0032+0.221/Re^0.237</text>
<text x="500" y="1100">0.0032</text>
</g>
</svg>
</body></html>
References
https://www.nuclear-power.com/nuclear-engineering/fluid-dynamics/major-head-loss-friction-loss/friction-factor-turbulent-flow-colebrook/
Friction Factor for Turbulent Flow – Colebrook Equation (2022)
..
For hydraulically smooth pipe and the turbulent flow (Re < 105), the friction factor can be approximated by the Blasius formula:
f = (100.Re)-¼
..
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 16:53, 11 October 2022 | 1,517 × 560 (28 KB) | T (talk | contribs) | <div style="margin:-18px -14px 0px -200px; background-color:#fff"> <div style="margin:0px 0px 0px 30px; line-height:1.2em"><br> Various approximations for the hydrodynamic resistance of a pipe versus the Reynolds number. The formulas are from... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.